Discharge Nursing Note

Discharge Nursing Note: A Comprehensive Guide
When a patient is ready to leave the hospital, a proper discharge nursing note must be prepared.
This note is an essential part of healthcare, and it ensures that both the patient and any future healthcare providers know the exact state of the patient’s health and what care has been provided.
Let’s explore this important subject in detail.
Introduction to the Discharge Nursing Note
A discharge nursing note is a document that summarizes a patient’s hospital stay and the care they received. It includes important information like the diagnosis, treatment provided, patient’s response, and follow-up care instructions.
Why is it Essential?
The discharge note plays a crucial role in providing continuity of care. It helps the patient and their family to know what to do next, and it ensures that healthcare providers who may later treat the patient will understand what has already been done.
Related Articles
WHOL medical abbreviation
What is rnc in nursing?
What is an agency nurse?
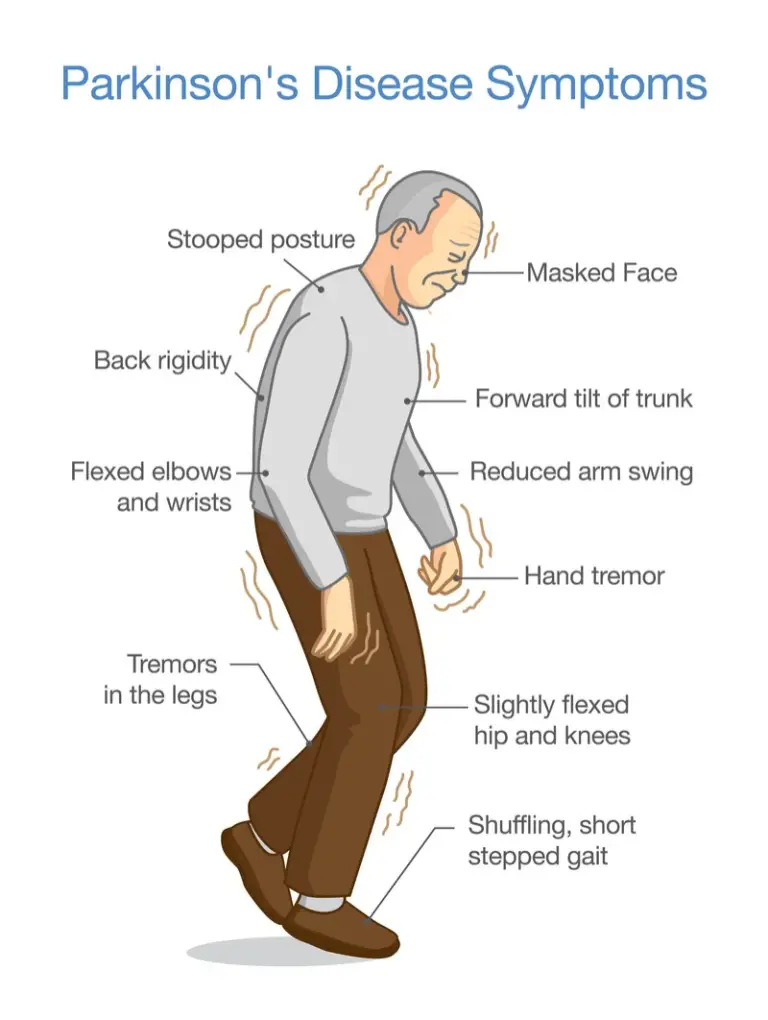
Parkinson’s disease nursing diagnosis
Discharge Nursing Notes
With advancements in technology, most electronic medical records (EMRs) now have a discharge process built into them. Here’s what that means:
1. Standardized Format
Most EMRs offer a standardized format for discharge notes. This helps nurses and doctors quickly fill out all the necessary information without forgetting any vital details.
2. Easy Access and Sharing
With EMRs, the discharge note can be easily accessed and shared among different healthcare providers. This ensures that everyone involved in the patient’s care is on the same page.
3. Patient Education
Modern discharge notes often include easy-to-understand instructions for the patient and their caregivers. This helps in ensuring that they know how to care for themselves or their loved one at home.
Key Elements to Include in a Discharge Nursing Note
Whether using an EMR or not, there are some general things that should always be included in a discharge nursing note:
Diagnosis and Treatment
Outline the patient’s diagnosis and the treatments they received during their stay.
Patient’s Response
Explain how the patient responded to the treatments.
Medications
List all the medications that the patient will need to continue taking after leaving the hospital.
Follow-up Care Instructions
Follow-up Care Instructions
Ongoing Treatment Needs
Explain any ongoing treatments, like physical therapy or dialysis, that must continue after discharge.
Scheduled Appointments
Provide information on scheduled follow-up visits with doctors or specialists. Include dates, times, and locations.
Home Care Guidance
Offer instructions on how the patient or caregivers should manage care at home, including wound care, diet, exercise, etc.
Contact Information
Primary Care Providers
Include names and contact information for the patient’s primary care doctors, nurses, or specialists involved in ongoing care.
Emergency Contacts
Provide emergency contact numbers that the patient or caregivers can use if urgent issues arise.
Specialty Care Contacts
If the patient needs to see any specific specialists, include their contact details.
Provide detailed instructions for any necessary follow-up care, like future doctor visits or therapy sessions.
Contact Information
Include contact information for the healthcare providers who will be involved in the patient’s ongoing care.
Conclusion
A discharge nursing note is more than just a summary of a hospital stay. It’s a critical document that ensures smooth transition of care from the hospital to home or another healthcare facility.
By taking advantage of modern EMRs with built-in discharge processes, healthcare providers can make this transition even more seamless.
In the end, the discharge nursing note is all about patient care. By being thorough, clear, and attentive to details, nurses and doctors can help ensure that the patient continues to receive the best possible care after they leave the hospital.
Whether using modern technology or traditional methods, the focus must always be on the patient’s health and well-being.
References
Phyllis Robinson MSN, RN is a Registered Nurse of 27 years. Phyllis is passionate about the prevention and healing of heart disease using traditional and alternative methods. She has experience in emergency room, telemetry, infusion, and critical care. Phyllis currently practices in an intensive care unit.